Egg deleup process is a important and elaborate biological method that takes place in the reproductive gadget of females across numerous species. For maximum animals, this method starts inside the ovaries and progresses through several stages earlier than the egg is either fertilized or laid. A deeper information of egg improvement not most effective offers insight into the workings of biology but additionally performs a extensive position in fields like agriculture, animal husbandry, and reproductive science.
Egg development refers back to the creation and maturation of an egg (or ovum) that, once fertilized, forms the muse for a new organism. In species like birds, this manner culminates inside the external laying of the egg, which ought to then undergo fertilization or be incubated to eventually hatch into a new life. The mechanisms at the back of egg development are essential to duplicate, influencing both natural and domesticated breeding processes.
By focusing at the various levels of egg formation, from its preliminary introduction inside the ovary to the very last ranges of fertilization or incubation, we will higher recognize its importance inside the reproductive cycle of many animals.
Understanding Egg deleup process in Female Organisms
Egg development is a captivating organic manner that plays a crucial role in duplicate throughout numerous species. In animals, together with birds, reptiles, and mammals, the formation of eggs is a extraordinarily specialised and complicated collection of occasions. Understanding how eggs develop is essential now not best for biological fans but also for the ones concerned in fields like agriculture, animal husbandry, and reproductive research.
The technique starts offevolved in the ovaries, wherein an egg, or ovum, begins its journey from an immature state to its full potential. Along the way, severa modifications occur, inspired by way of various biological and environmental factors. This article presents an in-depth exploration of egg development, protecting its anatomy, degrees of formation, and the large roles played by using hormones in making sure the survival and viability of the egg.
The Anatomy of the Egg
To definitely apprehend the system of egg development, it’s important to apprehend the important thing components that make up an egg. Regardless of the species, the shape of the egg is mainly designed to help the growing embryo and defend it for the duration of growth. Each part of the egg plays a vital function, operating together to ensure that the egg can grow to be a new organism or, if fertilized, serve as the place to begin for life.
At the center of the egg is the yolk, a nutrient-rich component that serves because the primary source of electricity for the developing embryo. Packed with vital nutrients, proteins, and fats, the yolk affords the nourishment necessary for the early levels of boom. It supplies the constructing blocks for cellular techniques and the electricity required for the embryo’s fast mobile division. Without a healthy, nutrient-wealthy yolk, the embryo would lack the assets needed for correct development.
Encasing the yolk is the egg white, or albumen, a clean, viscous substance that no longer only protects the yolk but also offers extra nutrients to aid the embryo. The albumen allows maintain the structural integrity of the egg at the same time as offering a strong surroundings for the yolk. It additionally acts as a cushion, lowering the hazard of physical harm to the yolk all through the egg’s adventure via the reproductive device.
Beneath the difficult shell, the egg is surrounded through skinny layers referred to as shell membranes. These layers serve an crucial protective function by way of preventing harmful bacteria from entering the egg, thereby safeguarding the growing embryo. Additionally, the shell membranes help hold the egg’s form and offer introduced guide to the developing embryo, ensuring its balance because it progresses through its development.
The outermost layer of the egg is the eggshell, frequently composed of calcium carbonate. This tough, defensive shell shields the embryo from environmental hazards, including bodily harm and pathogens, even as nevertheless bearing in mind critical gasoline change. Despite its electricity, the eggshell is porous sufficient to allow the embryo to respire all through incubation, permitting oxygen to go into and carbon dioxide to exit. The thickness and texture of the shell can vary relying on factors like species, the age of the chicken, and the nutritional content of its weight loss program, all of which make a contribution to the general safety and viability of the egg.
Key Stages of Egg Development

Egg improvement in birds follows a carefully orchestrated collection of tiers, with slight versions across species, but the popular development stays in large part constant amongst maximum avian species. The journey of egg development begins inside the ovaries, wherein the procedure starts with the advent of immature egg cells called ova. These ova continue to be dormant until hormonal indicators trigger their growth and maturation. For many fowl species, this procedure starts offevolved early in existence and keeps for the duration of the reproductive years of the animal.
Within the ovaries, the ova increase inner small, sac-like systems called follicles. As the ovum matures, it absorbs vitamins from the encompassing follicle, ensuring that it profits the vital power reserves for fertilization and destiny improvement. This level is essential because it guarantees that the egg has the proper nutrients to assist its survival after fertilization and as it movements thru the reproductive manner. Without those reserves, the egg might lack the energy wanted for proper embryonic improvement.
Once the ovum reaches complete adulthood, it’s far launched from the follicle in a method called ovulation. This launch is tightly regulated by hormones that manipulate the fowl’s reproductive cycle. For instance, in chickens, luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulates the rupture of the follicle, inflicting the mature ovum to be launched into the reproductive tract. At this factor, the egg is prepared to transport through the oviduct, in which further changes will take location. If mating has passed off previous to this stage, fertilization may additionally take location early on inside the oviduct, initiating the technique of embryonic development.
Journey Through the Oviduct
After ovulation, the egg embarks on its adventure thru the oviduct. This elongated tube-like structure is wherein the egg undergoes its maximum good sized transformations earlier than being laid.
- Infundibulum: The first segment of the oviduct is the infundibulum, in which sperm may fertilize the egg if mating has taken location. The egg spends a quick time right here earlier than shifting on.
- Magnum: The subsequent section, the magnum, is in which the egg white (albumen) forms across the yolk. This technique takes several hours and is vital for ensuring the egg is properly-cushioned for its journey.
- Isthmus: The isthmus is the a part of the oviduct where the membranes of the eggshell start to shape around the egg. These membranes assist guard the growing egg because it continues its direction.
- Uterus (Shell Gland): The final stage of the oviduct adventure is the uterus, also known as the shell gland. Here, the eggshell is deposited, giving the egg its outer protective layer. This is the stage wherein the eggshell gets its final thickness, and in some species, it can collect colour.
The complete procedure of journeying via the oviduct can take around 24 hours in many chook species.
The Formation of the Eggshell
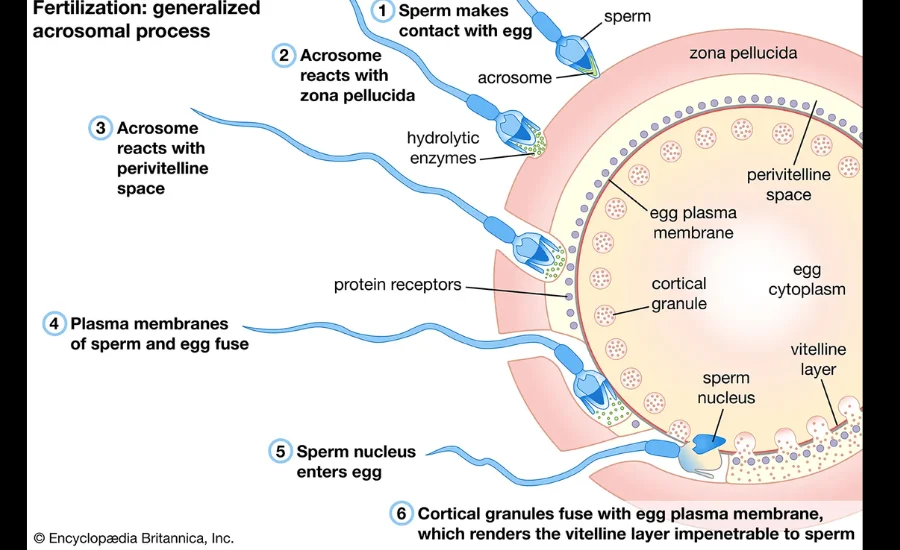
The creation of the eggshell is one of the maximum crucial tiers in egg improvement. Serving because the first line of protection for the developing embryo, the eggshell protects the egg from environmental threats, physical harm, and bacterial invasion. The shell is in general composed of calcium carbonate, a substance that imparts the pressure and durability necessary to safeguard the contents of the egg. Without a strong, intact shell, the egg could be noticeably at risk of outside elements that could compromise its viability.
For the eggshell to shape nicely, an adequate deliver of calcium is needed. This calcium is drawn from both the fowl’s bones and its diet, ensuring that sufficient is available for shell formation. As the calcium is absorbed, it’s far deposited around the membranes that surround the yolk, regularly forming a difficult, protecting shell. This manner is critical, as the strength of the shell gives now not simplest protection however also structural assist for the developing embryo.
The coloration and thickness of the eggshell can range relying on the species of hen. For example, chicken eggs can be white, brown, or maybe blue, with the shade being decided with the aid of the bird’s genetic makeup. The thickness of the shell also varies and is influenced by elements along with the chicken’s age, eating regimen, and overall fitness. A thicker shell gives better safety and is greater immune to cracking, supporting make sure the egg remains intact and stable because it movements through the reproductive manner. The cautious stability of calcium and different elements plays a essential position in generating an egg that is sturdy and capable of supporting the developing embryo inside.
Hormones and Egg Development
Hormones are essential for regulating the various tiers of egg development, ensuring that the process takes place smoothly and efficiently. These chemical messengers coordinate the complex organic approaches required for the formation of a healthy egg, in addition to the timing of its release. Estrogen, one of the primary hormones involved in the early stages, plays a pivotal role in egg development. It stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, the structures within the ovary wherein the eggs broaden. Estrogen additionally encourages the production of the yolk, that’s essential for nourishing the developing embryo as soon as fertilization occurs. By selling those early levels, estrogen allows put together the ovum for the following phases of improvement, including the opportunity of fertilization.
Once the ovum has matured, any other hormone, progesterone, takes over to facilitate the technique of ovulation. Progesterone helps put together the reproductive tract for the discharge of the egg. This hormone alerts that the egg is fully advanced and geared up to be launched from the ovary into the oviduct. The presence of progesterone ensures that the frame is prepared for this important moment within the reproductive cycle.
As the egg nears the very last stages of its development and is ready to be laid, oxytocin comes into play. This hormone is essential all through the egg-laying method, as it enables the muscle mass of the oviduct agreement. These contractions assist in moving the egg via the reproductive tract, making sure it is expelled from the fowl’s body at the proper time. The coordinated actions of these hormones—estrogen, progesterone, and oxytocin—make certain the egg develops properly and is laid in a well timed manner, contributing to the fulfillment of the reproductive cycle.
Fertilization and Embryonic Development
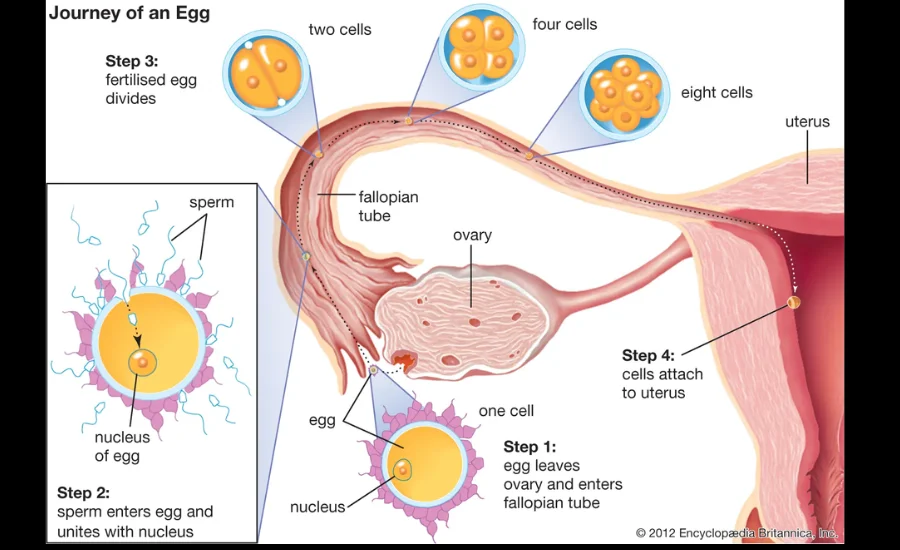
Egg development reaches its peak when fertilization occurs or when the egg keeps through its herbal life cycle. In the case of fertilization, the system leads to the formation of an embryo, a essential step within the reproductive cycle. Fertilization normally takes place rapidly after ovulation while the egg enters the oviduct. Here, sperm cells from the male are introduced into the lady reproductive machine, and if a hit, one sperm will enter the egg, ensuing inside the formation of a zygote. This zygote is a unmarried mobile shaped from the fusion of the sperm and egg, and from this factor, it starts offevolved to divide unexpectedly, growing into a multi-cell organism. As the fertilized egg actions via the reproductive tract, it undergoes in addition improvement, in the end forming a fully advanced embryo able to impartial existence.
Once the egg has reached full adulthood and undergone all necessary internal techniques, it begins its journey via the ultimate parts of the reproductive tract. This final phase involves hormonal signals and muscular contractions that push the egg thru the bird’s body. These contractions assist pass the egg thru the cloaca and out into the external environment, wherein the egg might be laid. This complete method, managed by means of a chain of hormonal cues, ensures that the egg is expelled on the proper time for both further development or, within the case of a fertilized egg, incubation.
In maximum hen species, egg laying follows a predictable cycle. For instance, hens typically lay an egg each 24 to 26 hours, a procedure this is exceedingly consistent and essential for preserving regular egg manufacturing, in particular in business farming operations. This regularity is important in agriculture, in which making sure a constant deliver of eggs is fundamental to meeting demand. The efficiency of this cycle highlights the complexity and precision of the reproductive system, making sure that egg production stays constant and sustainable. The complete procedure, from fertilization to egg laying, underscores the critical tiers that make a contribution to successful duplicate and the continuation of the species.
Post-Laying: Incubation and Embryo Development
After an egg is laid, its development maintains beneath specific situations. If the egg is fertilized, the technique of incubation starts offevolved, allowing the embryo internal to develop and finally change into a totally shaped organism. During incubation, the egg have to be saved at a specific temperature to make sure the embryo has the ideal surroundings to thrive. This temperature regulation is essential for keeping the right situations for the growing embryo, ensuring it has the strength and stability needed for persisted growth. Without proper temperature manipulate, the embryo won’t increase as anticipated, and in some cases, it can not live to tell the tale.
In addition to temperature, the egg’s shape performs a big function in facilitating the embryo’s improvement. The eggshell, which is both shielding and porous, permits for a essential change of gases. As the embryo grows, it wishes a non-stop supply of oxygen to fuel its metabolism and improvement. The eggshell’s pores permit oxygen to go into while simultaneously permitting the discharge of carbon dioxide, a waste product of the embryo’s metabolic processes. This gasoline change is critical for the embryo’s survival, as a buildup of carbon dioxide could suffocate the growing organism.
The exchange of gases via the eggshell is a finely tuned manner that ensures the embryo gets the oxygen it calls for even as maintaining a balance that helps its ongoing improvement. This exchange allows the embryo to grow at a consistent pace, in the long run main to the hatching of a brand new organism when the situations are most appropriate. The pleasant of the egg’s shell and the environment in which it’s miles incubated are, consequently, essential to the a hit boom and hatching of the embryo internal.
Factors Affecting Egg Quality

The exceptional of an egg is substantially impacted via a selection of factors, maximum appreciably the health of the fowl, its weight loss program, and the environmental situations in which it lives. A hen’s normal nicely-being plays a essential role in making sure that its eggs are of the best satisfactory. When a chook is healthy, it’s miles much more likely to provide eggs with sturdy shells, a right yolk-to-white ratio, and a steady shape, all of which are critical for the egg’s viability and achievement in hatching.
One of the key elements influencing egg high-quality is vitamins. A properly-balanced weight-reduction plan is essential for the chicken’s reproductive gadget and its capability to provide healthy eggs. Essential nutrients, inclusive of calcium, protein, and nutrients, are crucial for the proper formation of the egg, specially for the development of the eggshell. Calcium, as an example, is essential for creating a tough, defensive shell that safeguards the growing embryo. Protein affords the energy and constructing blocks for the egg’s additives, while nutrients ensure that the chook’s reproductive device functions nicely. When a bird suffers from dietary deficiencies, it may lead to susceptible or brittle eggshells, smaller yolks, or even a discount within the frequency of egg manufacturing.
In addition to nutrients, the hen’s environment plays an similarly important function in determining the satisfactory of its eggs. Environmental factors such as lighting fixtures, temperature, and universal dwelling conditions can all influence the chicken’s reproductive cycles. For instance, in commercial rooster farming, synthetic lighting fixtures is usually used to modify egg-laying cycles, making sure that hens continue to be productive for the duration of the 12 months. However, intense environmental situations—consisting of immoderate warmth or bloodless—can have adverse outcomes on each the amount and fine of the eggs. Overly high temperatures can strain the birds, main to irregular egg production and eggs with thinner shells, at the same time as extraordinarily cold conditions can slow down the egg-laying manner altogether. Therefore, keeping a strong and comfortable environment is crucial for optimizing egg production and ensuring terrific eggs.
Ultimately, the combination of right vitamins, desirable fitness, and a good surroundings creates the appropriate situations for the manufacturing of strong, healthy eggs. These elements paintings together to make sure that the egg isn’t simplest appropriate for hatching but also meets the standards required for intake, making the hen’s standard care and control critical to preserving egg fine.
Also Read: 0458 Password Easter Egg
Final Words
Egg development is a complex and essential system in reproduction throughout numerous species. It starts in the ovaries, in which immature egg cells, called ova, mature inside follicles, absorbing vitamins for future development. Once completely matured, the egg is released all through ovulation and travels thru the oviduct, present process good sized transformations. In the oviduct, the yolk is surrounded by means of albumen (egg white), and the eggshell membranes shape earlier than the shell is deposited in the uterus. Hormones adjust those ranges, making sure easy egg formation and release.
The eggshell, in general fabricated from calcium carbonate, affords safety for the embryo, while the albumen gives extra nutrients and cushioning. Fertilization, if it occurs, leads to embryo improvement. After laying, the egg should be incubated, keeping the right temperature for embryonic boom. Environmental elements like food regimen and situations influence egg first-class, impacting its viability and successful hatching. Thus, knowledge egg improvement is vital for each herbal and agricultural replica structures.
For the fine insights on egg development and extra, go to Discover Outlooks nowadays!
