Parenting Style Repartition Graph plays a vital role in shaping a child’s growth and development. Ever wondered how your approach stacks up against other parents? A parenting style distribution graph offers a clear view of how different parenting methods are represented across various groups, such as cultural, regional, or demographic segments.
This article will define a parenting style distribution graph, look at the four main parenting philosophies, and explain how to use this tool to assess and consider your own parenting style. This resource offers valuable viewpoints to help you better understand the effects of parenting styles, regardless of whether you are a parent or simply interested in child development.
Understanding the Parenting Style Repartition Graph
A Parenting Style Repartition Graph is a powerful visual tool that illustrates how various parenting approaches are distributed within a specific group. Typically, the graph divides parenting styles into four categories: authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and neglectful. It then shows the percentage of parents who fall into each category, making it easier to understand how different parenting strategies are spread across a population.
For instance, the graph may show that 10% of parents are negligent, 20% are permissive, 30% adopt an authoritarian style, and 40% use an authoritative approach. Researchers, psychologists, and even parents themselves can learn more about the common Parenting styles in a neighborhood or population by using these statistics.
Parents who wish to assess how their own parenting style stacks up against others would find such a graph particularly helpful. You can have a better understanding of the most popular approaches and see how your own strategy fits into the larger picture by looking at the distribution of parenting techniques.
The Four Key Parenting Styles and Their Impact
Parenting Style Repartition Graph are the emotional tone and strategies parents use to raise their children. Psychologist Diana Baumrind identified four distinct styles: authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and neglectful. Each of these styles represents different levels of responsiveness and expectations from parents, shaping how children grow and develop.
Warmth and discipline are balanced by authoritative parents. They set clear boundaries and expectations while fostering open communication, creating an environment where children feel supported and capable. This style often results in children who are confident, socially skilled, and well-adjusted.
In contrast, authoritarian parents prioritize strict obedience and control. They enforce rigid rules without much room for discussion or flexibility. Children raised in this environment may comply with rules but often face challenges with self-esteem, independence, and social relationships.
Conversely, permissive parents are kind and accommodating but don’t enforce many regulations. They frequently allow kids too much independence, which fosters creativity but occasionally leaves out important framework. Learning responsibility and self-discipline may become challenging as a result.
Lastly, parents who neglect their children don’t interact with them or hold them to high standards. Children may feel abandoned, uneasy, and alienated as a result of this neglect. Interpreting how various approaches affect child development and how they are represented in tools such as the parenting style distribution graph requires an understanding of these parenting philosophies.
Insights from the Parenting Style Repartition Graph
The Parenting Style Repartition Graph is a valuable tool for visualizing how different parenting styles are spread across various populations and cultures. By examining the distribution, we can gain a deeper understanding of societal norms and the cultural factors that influence how parents raise their children.
Cultural Influence on Parenting
Parenting styles are often shaped by cultural values and societal expectations. For example, in cultures that emphasize respect for authority and hierarchy, authoritarian parenting may be more common. On the other hand, in cultures that place a high value on individuality, permissive parenting might be the norm. Recognizing these cultural influences helps parents appreciate the diversity of parenting styles around the world and see how their own approach fits into the broader cultural context.
Shifting Societal Trends
The distribution graph can also reveal shifts in societal attitudes toward parenting. As new research highlights the importance of mental health and emotional well-being, we may see a rise in authoritative parenting approaches, which focus on support and structure. Keeping an eye on these trends helps parents stay informed and adapt to evolving best practices, ensuring they make choices that align with current knowledge and community values.
Reflecting on Your Parenting Style
Last but not least, the parenting style distribution graph offers a chance for introspection. You can determine whether your parenting style is in line with your own ideals and objectives by contrasting it with those depicted in the graph. This self-evaluation promotes development and progress, enabling you to modify your approaches to best promote the growth and welfare of your child.
Creating a Custom Parenting Style Distribution Graph

If you’re curious about the parenting styles in your own community, creating a personalized parenting style distribution graph can offer valuable insights. Begin by designing a survey to gather data on parenting approaches from friends, family, or community members. Tools like Google Forms or other survey platforms make it easy to collect responses efficiently. Once you’ve gathered the data, use graphing tools like Excel or Google Sheets to create a clear, visual representation of the results. This custom graph will give you a deeper understanding of parenting trends specific to your area, helping you explore how different styles are practiced in your community.
The Value of the Parenting Style Distribution Graph
The parenting style distribution graph is a helpful tool for parents looking to better understand their own parenting behavior. Parenting often requires balancing different approaches, and this graph can provide clarity by highlighting a parent’s strengths and areas that may need improvement. By breaking down various parenting styles, the graph offers insight into how each one affects a child’s development.
For instance, if a parent notices their graph heavily leans towards authoritarian methods, it may prompt them to consider introducing more warmth and support into their approach. On the other hand, if permissiveness is dominant, the parent might recognize the need to add more structure and discipline to better guide their child’s growth. This self-awareness fosters growth and refinement in parenting, helping parents make more informed decisions.
Benefits of Using a Parenting Style Distribution Graph
The parenting style distribution graph offers several valuable benefits for parents. It provides a clearer understanding of one’s parenting dynamics, recognizing that every family is unique. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, this graph gives parents a personalized view of how different parenting styles are combined within their household.
The graph also helps parents identify areas that may need adjustment. If a parent notices that certain parenting styles dominate and their child isn’t responding well, the graph can highlight potential imbalances. This insight allows for targeted changes that align more closely with the child’s individual needs.
Furthermore, the graph promotes consistency in parenting, which is crucial for raising well-adjusted children. By encouraging a balanced approach, it helps parents maintain a harmonious blend of discipline and emotional support, fostering healthy growth and development.
Interpreting the Parenting Style Repartition Graph
To accurately interpret a Parenting Style Repartition Graph, it’s important to understand its key components. The graph typically features two axes: the vertical axis represents responsiveness, which measures how emotionally supportive and nurturing parents are, while the horizontal axis indicates the level of demands, reflecting the expectations parents place on their children.
The intersection of these axes forms four distinct quadrants, each representing a primary parenting style. Authoritative parents, who maintain high responsiveness and high demands, occupy one quadrant. Authoritarian parents, characterized by low responsiveness and high demands, are placed in another. Permissive parents, marked by high responsiveness but low demands, fall into a different quadrant, while neglectful parents, who show low responsiveness and low demands, are positioned in the final quadrant. Understanding these components can provide valuable insights into parenting trends and their potential impact on child development.
Factors Shaping Parenting Style Repartition Graph
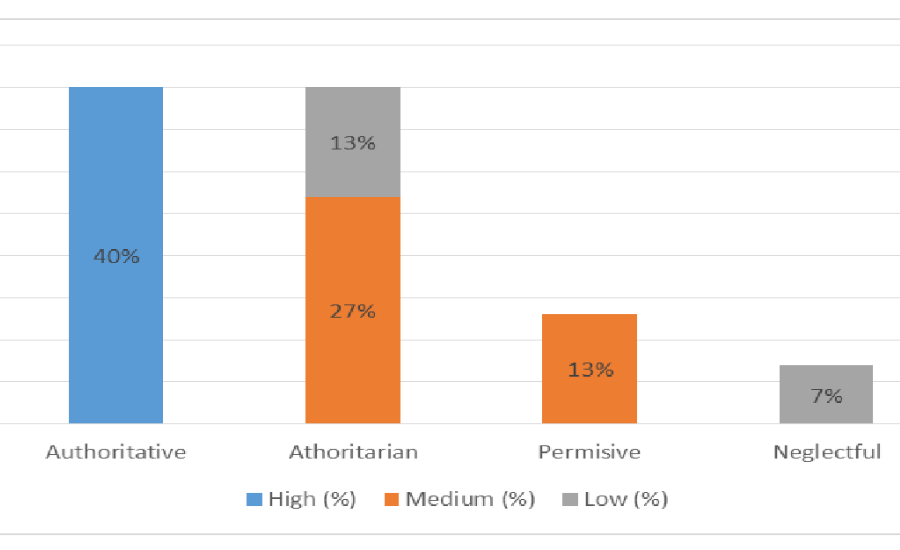
Parenting Style Repartition Graph are influenced by a variety of factors that shape how parents interact with their children. One key factor is socioeconomic status. Families with higher income levels often have access to more resources, such as education, healthcare, and support systems, which can promote authoritative parenting. In contrast, parents with fewer financial resources may experience increased stress, which can sometimes result in more authoritarian or neglectful approaches.
Cultural beliefs also play a significant role in shaping parenting practices. Different cultures have unique perspectives on child-rearing, which can lead to variations in parenting styles. For instance, collectivist cultures often emphasize obedience and family cohesion, leading to more authoritarian parenting. On the other hand, individualistic cultures prioritize independence and self-expression, which can align more with permissive parenting.
The educational background of parents is another influencing factor. Educated parents are generally more informed about child development theories and the benefits of authoritative parenting. This knowledge often encourages practices that foster open communication and mutual respect. Understanding these various influences is crucial for interpreting the differences in parenting styles, as reflected in the parenting style distribution graph.
Limitations of the Parenting Style Repartition Graph
While the Parenting Style Repartition Graph offers valuable insights, it is important to recognize its limitations. One key issue is potential bias in data collection. The accuracy of the graph depends on how representative the data sample is. If the sample doesn’t reflect a diverse range of demographics, the results may not accurately represent the broader population’s parenting styles.
Additionally, categorizing parenting styles into distinct types can oversimplify the complexities of human behavior. Parenting is not static; parents often adapt their approach based on various circumstances or the developmental stages of their child. A rigid classification system may fail to capture the nuances that influence parenting effectiveness.
Lastly, the graph should not be seen as the sole indicator of child outcomes. While it can highlight trends, numerous other factors—such as peer influence, educational systems, and individual child characteristics—play a significant role in a child’s development. Being mindful of these limitations ensures a more accurate understanding of the parenting style distribution graph and its implications.
Final Words
A parenting style repartition graph is a powerful tool that helps visualize how different parenting approaches are distributed across various groups or populations. It breaks down parenting into categories such as authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and neglectful, showing how each style is represented in specific communities or demographics. By examining this graph, parents and researchers can gain valuable insights into the prevalent parenting practices in a given area. It highlights trends and allows individuals to reflect on their own parenting approach, fostering self-awareness and growth. However, it’s important to recognize its limitations, such as potential biases in data collection and the oversimplification of complex parenting behaviors. The graph should be viewed as a helpful tool for understanding patterns, but not as the sole factor in determining child development. Understanding the broader context and multiple influences on parenting can lead to a more nuanced interpretation of the parenting style repartition graph.
For More Info Check It Out Discoveroutlooks